As requested here's the packed data and a test bench you can test your own merging function ideas and replicate my results (hopefully). If you want the plots you can use the end part of scripts in part1 part2.
The data is a bunch of super secret Eve Online killmails. The first part of the script handles the json to data.frame transformation. After that I introduce the R core merging in a for-loop, data.table variant, reduce function variants, and finally the fast.merging. There's actually alot more data then we are using in the bench. Totalling 166106 killmails, merging only 3000 of those. That is because as noted in previous posts the merge for-looping seems to work in exponential time so going much higher then 3000 lines seems really excessive. Even now it took over an hour to run the whole bench on intel i5 3570k (not overclocked). So if you want faster results choose 1000ish frames and set rbenchmark replications to 1. With low frame count (under 100) the results are fairly similiar.
If you are going to test are the results from different functions the same, note that the order of rows and columns will be different. I'm eagerly waiting for you results and ideas.
2013-03-24
2013-03-21
RMark: data.table merge vs core merge
This is the third post concerning fast merging in R, first here and second here. This time we are going to look at how the merge function from data.table package works in our case, requested by Uwe Block.
As a reminder the first post concerns doing a merging scheme using the lapply function. After that in the second post we looked how it translates to a parallel solution for even more speed.
As a reminder the problem is the following: given N amount of files with a random amount of variables in each file. How do we merge these files into a complete data within reasonable amount of time? For example you can consider that the medical instruments records it's each run (patient) to a different file. With only the values measured by the instrument are recorded to the file.
In practice I'm using Eve Online killmails. So far I have around 160k mails. Hence the need for a fast solution.
Personally I haven't really used data.table, but it looks good enough. So I recommend checking it out. But in a sense nothing's really changed on my code part. I did a fast merging function based on data.table merge called the lady, but won't give the code because it isn't fast enough (spoiler alert). Also the data.table merge is a generic function. Meaning if you are using data.tables in a merge it automaticaly uses the data.table merge function. But enough it this prattle. Here's the results.
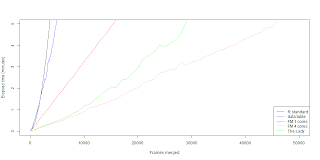
data.table merge is faster then the R core merge function if you are merging a for-loop solution. The problem still is that the data.table merging in a for-loop works in exponential time. Which doesn't translate well for big data. The single core fast merging scheme still beats the data.table merge in a for-loop. The biggest wonder is why when we combine the data.table merge with parallel fast merging scheme we get a slower outcome. Naturally I though we could squeeze few seconds out with low frame count, but seems that it's actually few minutes worse. So far I'm running dry in practical ideas and reasons why the lady seems so fat. Maybe it doesn't cleane up it's diet ? (memory management?) If you have some insight please comment.
As requested, here's the bench.
As a reminder the first post concerns doing a merging scheme using the lapply function. After that in the second post we looked how it translates to a parallel solution for even more speed.
As a reminder the problem is the following: given N amount of files with a random amount of variables in each file. How do we merge these files into a complete data within reasonable amount of time? For example you can consider that the medical instruments records it's each run (patient) to a different file. With only the values measured by the instrument are recorded to the file.
In practice I'm using Eve Online killmails. So far I have around 160k mails. Hence the need for a fast solution.
Personally I haven't really used data.table, but it looks good enough. So I recommend checking it out. But in a sense nothing's really changed on my code part. I did a fast merging function based on data.table merge called the lady, but won't give the code because it isn't fast enough (spoiler alert). Also the data.table merge is a generic function. Meaning if you are using data.tables in a merge it automaticaly uses the data.table merge function. But enough it this prattle. Here's the results.

data.table merge is faster then the R core merge function if you are merging a for-loop solution. The problem still is that the data.table merging in a for-loop works in exponential time. Which doesn't translate well for big data. The single core fast merging scheme still beats the data.table merge in a for-loop. The biggest wonder is why when we combine the data.table merge with parallel fast merging scheme we get a slower outcome. Naturally I though we could squeeze few seconds out with low frame count, but seems that it's actually few minutes worse. So far I'm running dry in practical ideas and reasons why the lady seems so fat. Maybe it doesn't cleane up it's diet ? (memory management?) If you have some insight please comment.
As requested, here's the bench.
2013-03-03
RMark: Parallel fast merging
Last time we looked at a different method of merging multiple files via fast mergin g. I highly recommend checking the fast merging function before we will translate it to a parallel solution. Parallel programming in this case means we are using more then one processor core. So even if you have a fancy 8 core machine R only uses one core if you don't use parallel functions.
In R parallel programming can be done for example with snow package. When we change our function from 1 core solution to a multicore solution we use snow packages parLapply function instead of lapply function. This change will magically make our independent loops run faster without doing any major changes to the script. As parLapply behaves almost exactly the same as lapply. So let us present the script first, the explanation will be given after that. There's alot more case handling in multicore case as we can't call our multicore solution if we only need one core.
For example if we have 100 frames to merge and a 4 core machine. We choose a section size of 25 parts (nparts=25). Which means that we have 4 sections. Section 1 will be frames from 1-25, section 2 will be frames 26-50, and so on. Now we tell the first core to merge the frames from section 1, the second core will merge frames outlined in section 2, and so on. After that is done we only have 4 frames, which can we will merge using the standard way. With this fast merging should atleast two times faster when using 2 cores. Let us see if that is the case, unfortunately I only have 4 cores.
In R parallel programming can be done for example with snow package. When we change our function from 1 core solution to a multicore solution we use snow packages parLapply function instead of lapply function. This change will magically make our independent loops run faster without doing any major changes to the script. As parLapply behaves almost exactly the same as lapply. So let us present the script first, the explanation will be given after that. There's alot more case handling in multicore case as we can't call our multicore solution if we only need one core.
For example if we have 100 frames to merge and a 4 core machine. We choose a section size of 25 parts (nparts=25). Which means that we have 4 sections. Section 1 will be frames from 1-25, section 2 will be frames 26-50, and so on. Now we tell the first core to merge the frames from section 1, the second core will merge frames outlined in section 2, and so on. After that is done we only have 4 frames, which can we will merge using the standard way. With this fast merging should atleast two times faster when using 2 cores. Let us see if that is the case, unfortunately I only have 4 cores.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)